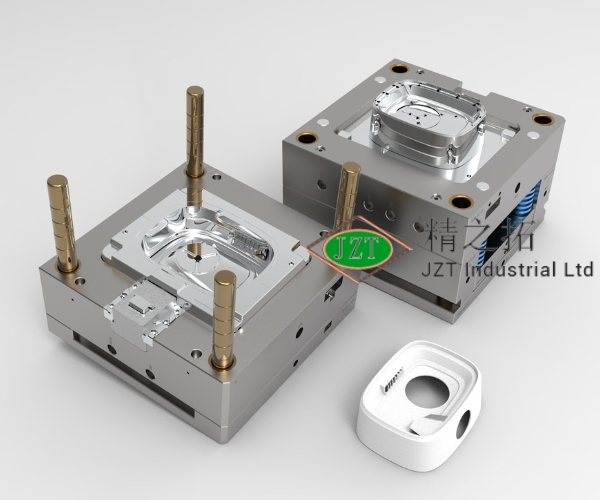
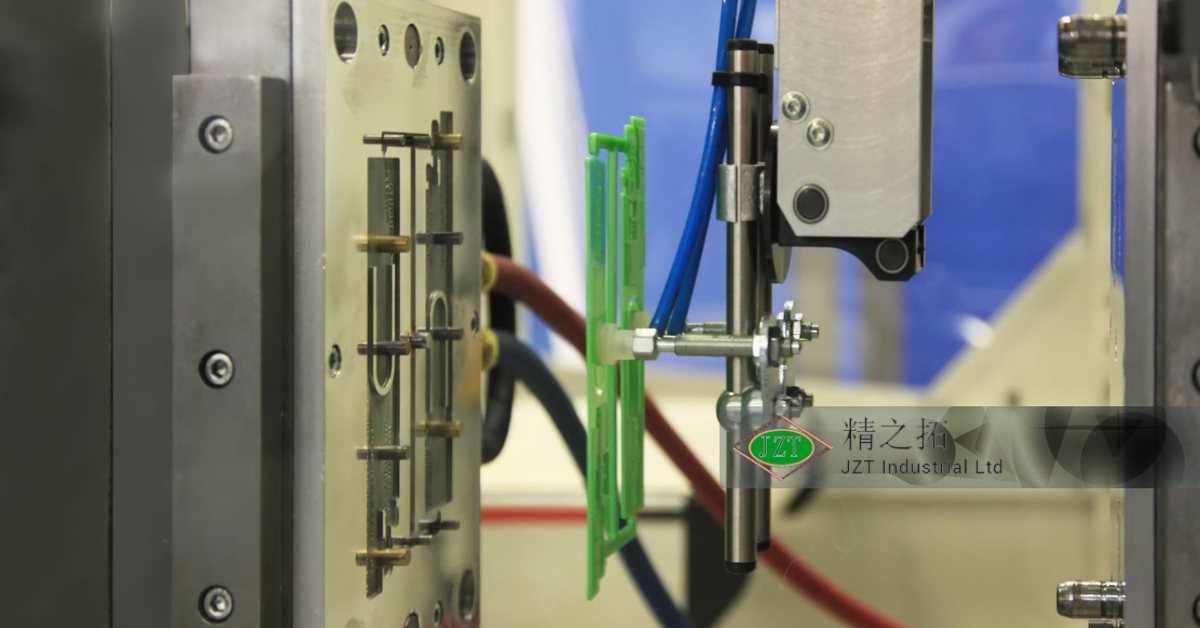
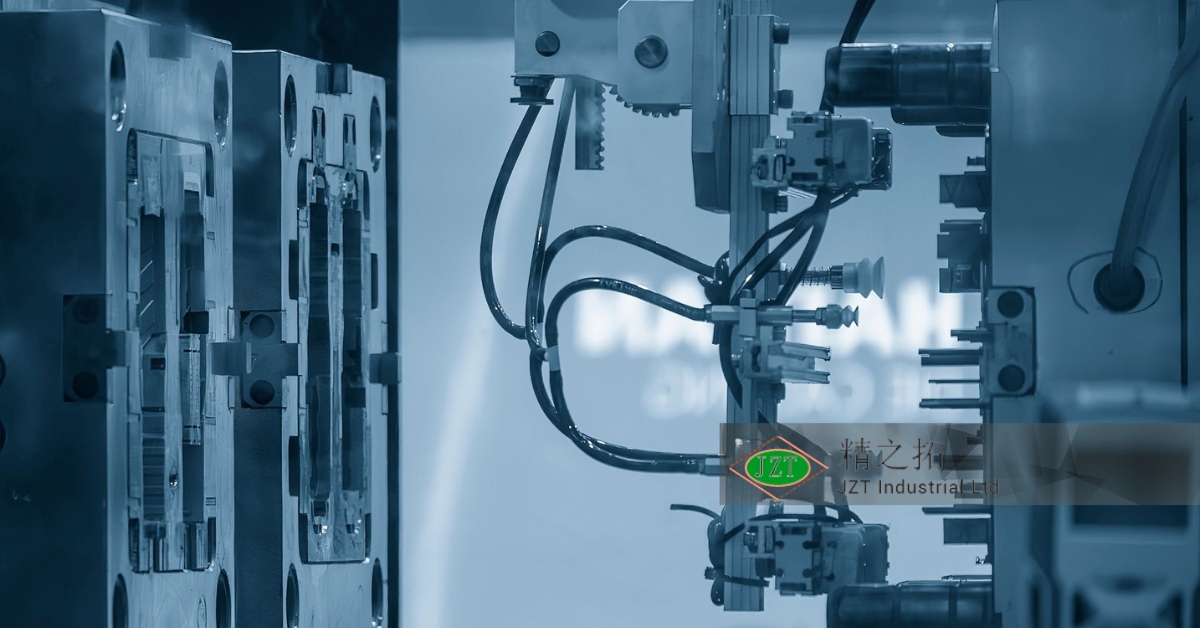
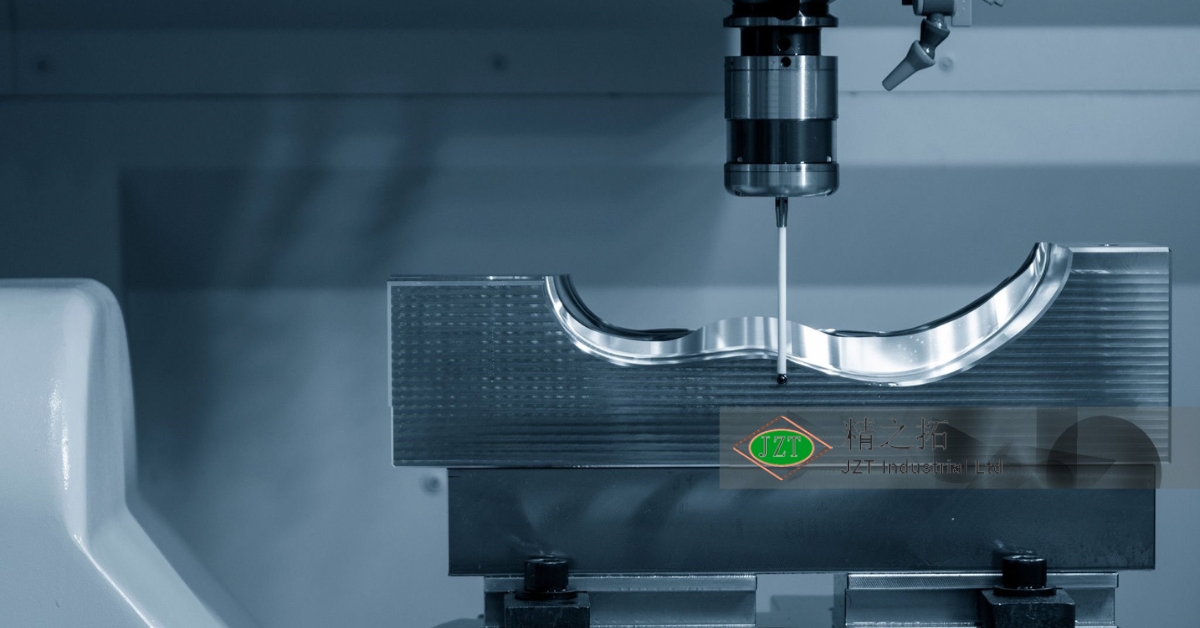
Introduction
Injection mold maintenance and care is critical for ensuring the longevity, performance, and cost-effectiveness of plastic injection molds. These molds are at the heart of producing high-quality custom plastic parts, and their condition directly impacts production efficiency, part consistency, and overall manufacturing costs. Without proper maintenance, molds can deteriorate, leading to increased downtime, reduced product quality, and costly repairs.
For plastic parts manufacturers, mold longevity is more than a matter of convenience; it’s an essential aspect of business profitability and product quality. By implementing structured maintenance practices, manufacturers can prolong mold life, reduce repair costs, and maintain consistent quality across production runs. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of mold care, the different types of maintenance, and practical steps manufacturers can take to ensure their molds remain in excellent condition for years to come. This guide is designed to offer actionable insights for any facility looking to maximize their injection mold investment.
Why Injection Mold Maintenance is Essential
Maintaining plastic injection molds is vital for ensuring consistent quality, minimizing production downtime, and reducing overall operational costs. Injection molds are often complex, high-value assets that endure substantial wear and tear during production, particularly in high-volume environments. The effects of neglecting proper injection mold maintenance and care are not only immediate but also cumulative, as even minor issues can develop into significant problems if not addressed promptly.
Understanding the Importance of Mold Care
Neglecting mold care can lead to severe consequences for a plastic parts manufacturer. Over time, issues such as misalignment, corrosion, or wear on mold surfaces can cause parts to develop defects, compromising their precision and quality. Moreover, mold-related issues can result in production stoppages, which lead to costly delays and impact overall productivity. The mold’s condition plays a critical role in maintaining production efficiency, as well-maintained molds ensure smooth operations, fewer interruptions, and reduced dependency on costly repairs or replacements. By prioritizing mold care, manufacturers effectively safeguard their production flow and ensure that every batch meets the required standards.
Impact on Product Quality and Consistency
For manufacturers producing custom plastic parts, maintaining high standards of quality is essential, and the mold’s condition directly affects the consistency of each part. A well-maintained mold will yield parts with the exact dimensions, surface finish, and structural integrity required, ensuring a consistent final product. Conversely, molds that are poorly maintained often result in defects such as flash, warpage, and parting line mismatch, leading to wasted materials and a greater likelihood of rejected parts. Regular maintenance keeps molds in peak condition, supporting quality control and delivering reliable, high-quality products that meet customer expectations.
Cost Savings Over Time
While maintenance may seem like an additional expense, it ultimately saves money by preventing more costly repairs and replacements. Proactively addressing minor issues before they escalate reduces the need for extensive repairs or entire mold replacements, both of which are time-consuming and expensive. Routine maintenance also extends mold life, reducing the frequency with which new molds need to be manufactured. This long-term approach to mold care is not only cost-effective but also improves the financial stability of production operations, as resources are allocated more efficiently.
Understanding the Types of Mold Maintenance
Different types of mold maintenance can be employed depending on the needs of the mold and production schedules. Each type offers unique benefits, allowing manufacturers to approach injection mold maintenance and care in a way that balances preventive care with responsive action.
Preventative Maintenance (PM)
Preventative maintenance is one of the most commonly employed strategies for mold care. It involves regularly scheduled inspections and routine tasks, such as cleaning, lubrication, and minor adjustments. The goal of preventative maintenance is to detect and address potential issues early on, preventing them from developing into significant problems. Tasks may include inspecting venting systems, ejector pins, cooling channels, and checking for buildup of residue or debris on the mold surfaces. Preventative maintenance minimizes the risk of unexpected mold failures and keeps molds running smoothly, resulting in consistent part quality and reduced production interruptions.
Predictive Maintenance (PdM)
Predictive maintenance is a more advanced approach that leverages monitoring tools and data to predict when a mold may require servicing. Sensors and tracking systems monitor key mold performance indicators, such as cycle counts, temperature, and pressure, to detect signs of wear before they become critical. By using predictive maintenance, manufacturers can proactively schedule repairs during planned downtime, preventing unplanned stoppages and ensuring that molds remain in optimal condition. Predictive maintenance also extends mold life by addressing wear-related issues early, reducing the overall wear-and-tear on critical components.
Reactive Maintenance
Reactive maintenance, also known as corrective maintenance, is conducted when a mold fails or shows visible signs of malfunction. While this type of maintenance is essential for addressing unexpected breakdowns, it should ideally be minimized in favor of preventative and predictive strategies. Reactive maintenance often leads to production delays and is typically more costly, as it requires urgent attention and potentially extensive repairs. However, in some cases, reactive maintenance can be used effectively to respond to minor issues that do not immediately impact production.
Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM)
Condition-based maintenance (CBM) relies on monitoring the specific conditions of the mold, such as temperature, humidity, and operational frequency, to determine when maintenance is needed. Unlike preventative maintenance, which is based on a schedule, CBM takes into account the actual wear conditions the mold experiences. By only performing maintenance when certain conditions are met, CBM optimizes the use of resources and reduces unnecessary interventions. This approach is especially beneficial for molds with varying operational demands, as it ensures that maintenance activities align with actual usage.
Routine Maintenance Checklist for Injection Molds
A structured maintenance routine helps manufacturers keep their molds in excellent condition and extends mold life. Here’s a breakdown of maintenance tasks based on frequency:
Daily and Weekly Maintenance
After each production run, it’s crucial to perform quick visual inspections and minor maintenance tasks. This includes cleaning mold surfaces to remove any residual plastic material, inspecting for any visible signs of wear, and checking for any buildup around the ejector pins or parting lines. Small issues, such as residue or loose bolts, can easily be addressed during this time, preventing them from impacting the next production cycle. Daily and weekly maintenance helps ensure consistent quality and uninterrupted production.
Monthly and Quarterly Maintenance
More in-depth inspections are conducted monthly or quarterly, depending on the mold’s usage. These inspections focus on critical components, such as cooling channels, ejector systems, and venting systems, to identify any wear that may affect mold performance. This is also the time to apply lubricants to moving parts, tighten bolts, and check for alignment issues. By performing monthly and quarterly maintenance, manufacturers can prevent minor issues from escalating into major problems and ensure each mold’s optimal performance.
Annual and Long-Term Maintenance
Annual maintenance involves comprehensive mold disassembly and inspection. During this time, all components are carefully inspected for signs of wear and tear, with worn parts such as springs, bushings, and guide pins replaced as necessary. This is also an opportunity to document the mold’s condition and maintenance history, which can provide valuable insights for future maintenance planning. Annual maintenance is a critical step in prolonging mold life, ensuring that all parts are in top condition for high-quality, uninterrupted production.
Key Areas of Focus in Injection Mold Maintenance
Effective injection mold maintenance and care requires attention to several key areas to prevent common issues and extend mold life.
1. Cleaning and Lubrication
Proper cleaning and lubrication are fundamental aspects of mold maintenance. Cleaning removes buildup of plastic residue, debris, or any other contaminants that could affect mold quality. The choice of cleaning agent depends on the material used and the specific requirements of the mold, with care taken to avoid harsh chemicals that could damage surfaces. Lubrication is equally important, as it reduces friction and prevents corrosion on moving parts, such as ejector pins and guide rails. Ensuring that lubrication is applied regularly will help prevent unnecessary wear and ensure smooth mold operation.
2. Mold Alignment and Parting Line Integrity
Maintaining proper mold alignment is essential to prevent parting line wear and ensure that each part produced meets quality standards. Misalignment can lead to issues like flash, which can negatively impact product quality and increase waste. Regular inspections and alignment adjustments, using specialized tools if necessary, can help maintain parting line integrity and prevent mold misalignment over time.
3. Cooling Channels and Temperature Regulation
The cooling system is a critical component of injection molds, as it directly affects cycle times, part quality, and the overall efficiency of the molding process. Blocked or inefficient cooling channels can lead to uneven cooling, causing warpage or other defects in the parts produced. Routine flushing and cleaning of cooling channels help maintain optimal temperature regulation and prevent blockages, reducing cycle times and ensuring uniform cooling.
4. Ejector System Maintenance
Ejector pins, sleeves, and return springs play a vital role in the smooth ejection of parts from the mold. Regularly inspecting and maintaining these components helps avoid issues such as bent or worn pins, which can cause part ejection problems or damage the mold. Ejector system maintenance also includes checking alignment and lubrication to ensure consistent, problem-free ejection.
5. Venting System Maintenance
Proper venting is crucial for avoiding defects like burn marks or incomplete fills caused by trapped air. Over time, vent channels can become clogged, reducing their effectiveness. Regular cleaning and re-cutting of vents as part of routine maintenance prevent these issues, ensuring that air escapes smoothly and that parts are produced with clean surfaces and accurate dimensions.
Conclusion
Proper injection mold maintenance and care is an essential practice for any plastic parts manufacturer aiming to prolong the life of their molds, ensure consistent product quality, and reduce overall costs. By implementing a structured maintenance routine that includes daily, weekly, and annual tasks, manufacturers can address issues proactively, minimizing downtime and repair costs. Key focus areas, such as cleaning, lubrication, mold alignment, and cooling channel maintenance, are vital for preventing mold wear and preserving part quality.
As the demand for high-quality, durable custom plastic parts continues to grow, the importance of well-maintained molds becomes even more critical. Injection molds are valuable assets that require attention and care to perform at their best. By investing in proper mold maintenance, manufacturers not only extend mold life but also create a more efficient, productive, and profitable manufacturing environment. Adopting best practices for injection mold maintenance is a smart, proactive approach that pays dividends in the long term, providing consistent, high-quality output and reduced operational costs.
FAQs
What is the best way to maintain injection molds?
The best way to maintain injection molds includes a combination of preventative, predictive, and condition-based maintenance. This approach ensures regular inspections, cleaning, and lubrication, addressing issues proactively and keeping molds in optimal condition for long-term use.
How often should injection molds be serviced?
The frequency of servicing depends on production usage. Daily and weekly checks are essential for surface cleaning and minor adjustments, while in-depth monthly, quarterly, and annual inspections are recommended for more thorough maintenance, such as component replacement and alignment checks.
What are the signs that an injection mold needs maintenance?
Signs that a mold needs maintenance include visual wear, such as surface discoloration or corrosion, functional issues like flash, part misalignment, or inconsistent dimensions, and abnormal noises during operation. Monitoring cycle counts and performance indicators also help identify when maintenance is needed.
What types of cleaning agents are safe for injection molds?
Cleaning agents should be chosen based on the mold material and any residues present. Non-abrasive cleaners that do not damage mold surfaces are generally recommended. For sensitive molds, mild, mold-specific cleaning agents are advised to avoid corrosion or wear.
Can predictive maintenance help reduce mold repair costs?
Yes, predictive maintenance significantly reduces mold repair costs by detecting signs of wear early, allowing manufacturers to address issues before they escalate. This approach prevents unexpected breakdowns, minimizes repair frequency, and extends the life of the mold.