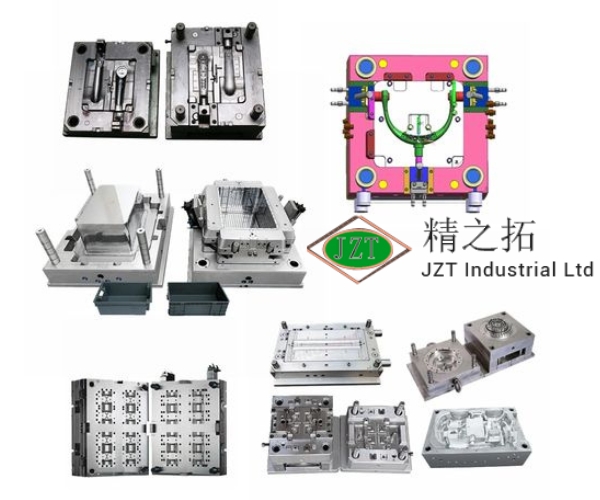
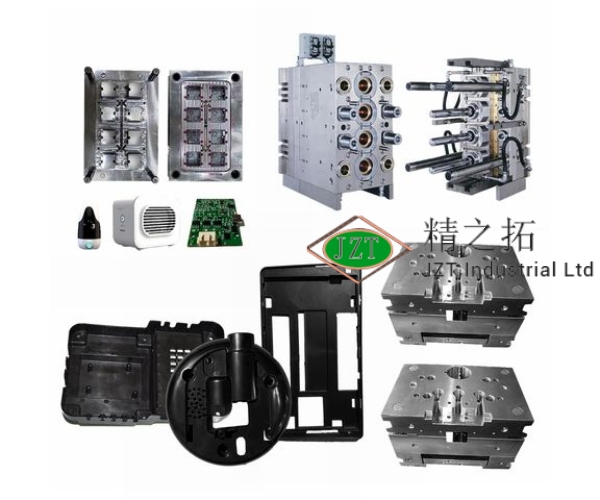
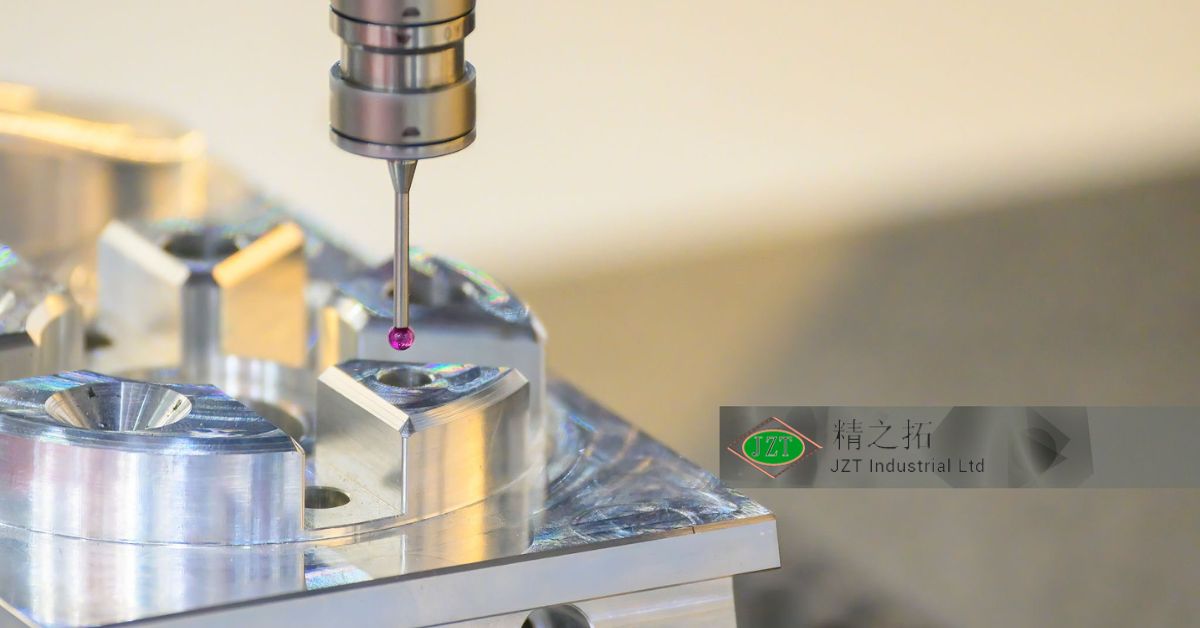
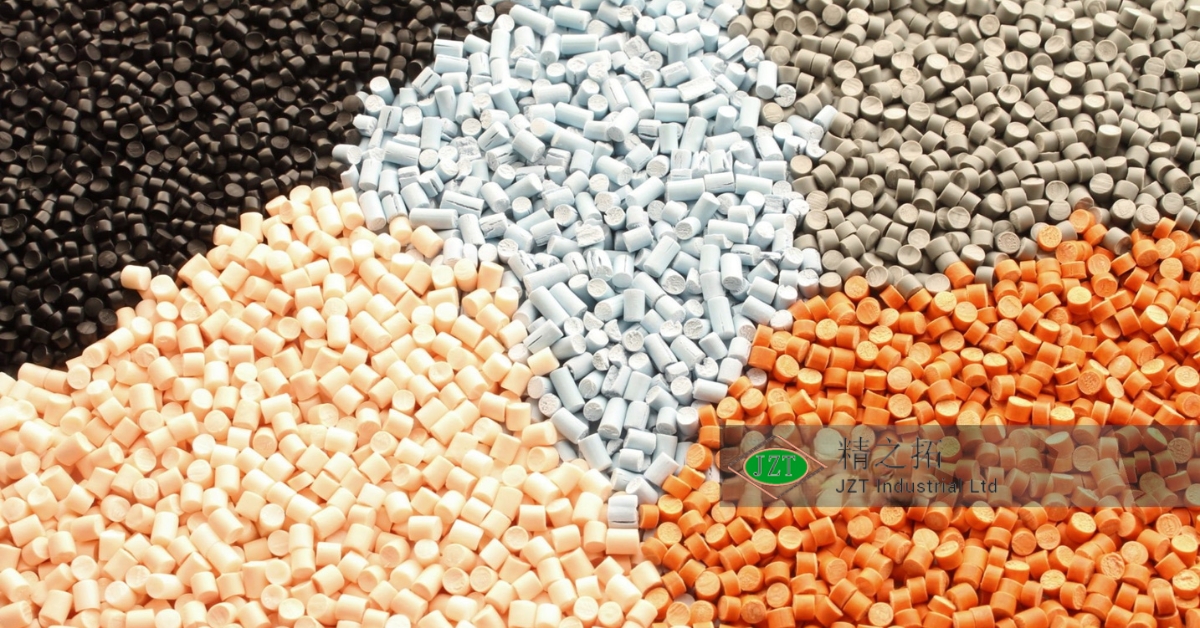
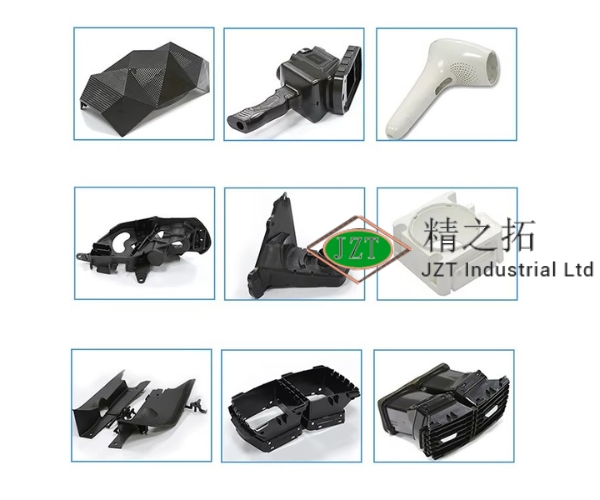
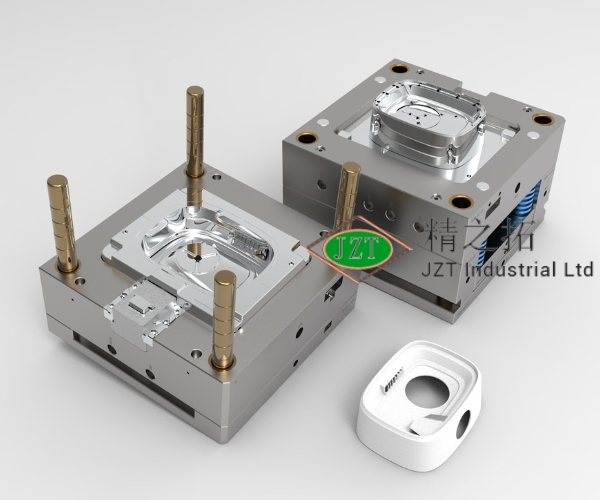
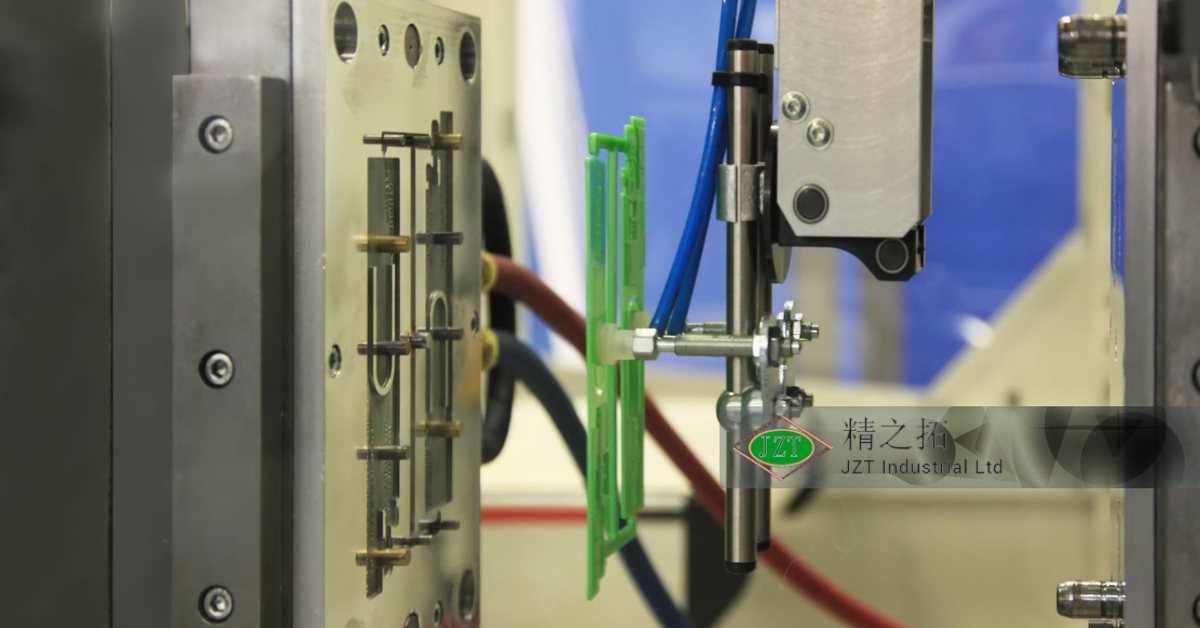
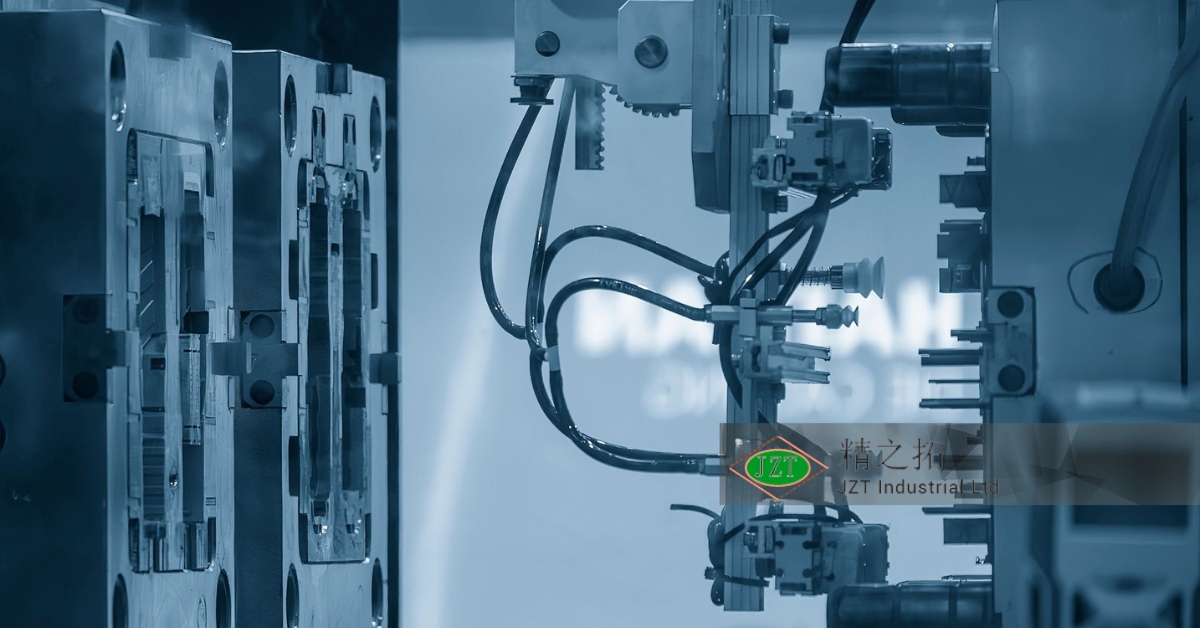
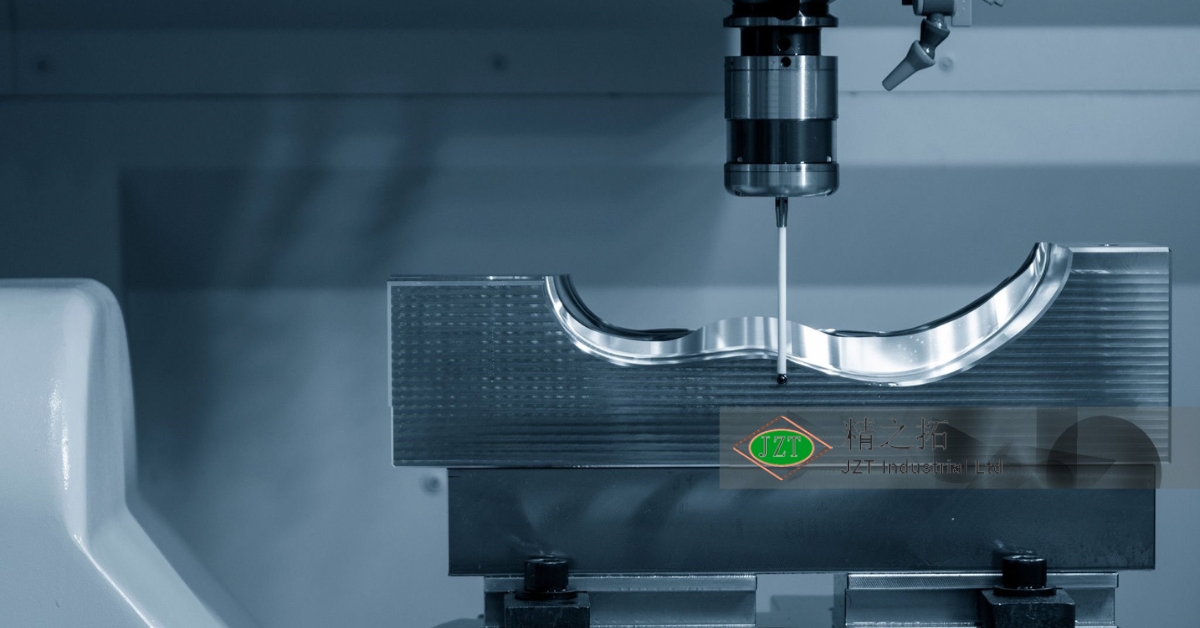
Overview of Plastic Injection Molding Parts
Plastic injection molding parts are an integral part of modern manufacturing, found in nearly every industry from automotive and electronics to healthcare and consumer goods. These parts are produced through a process called plastic injection molding, where molten plastic is injected into a mold cavity and then cooled to form a solid part. The versatility, precision, and scalability of this process make it the preferred method for producing a wide variety of plastic components.
Understanding what plastic injection molding parts are, how they are made, and where they are used is essential for anyone involved in manufacturing or product development. Whether you are a designer looking to create new products, a business owner seeking efficient manufacturing solutions, or simply curious about how everyday objects are made, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive overview of plastic injection molding parts.
In this complete guide, we will explore the fundamentals of plastic injection molding, the types of parts that can be produced, design considerations, the detailed process of injection molding, and much more. By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of plastic injection molds and the critical role they play in modern manufacturing.
Purpose of the Guide
This guide is designed to be an all-encompassing resource for anyone interested in plastic injection molds and the parts produced through this process. Whether you are new to the field or looking to deepen your knowledge, this guide will help you understand the complexities of plastic injection molding and how it applies to various industries.
We will cover everything from the basics of the injection molding process to the latest trends and innovations in the field. You will learn about the different types of plastic parts that can be produced, the design principles that ensure quality and efficiency, and how to choose the right plastic parts manufacturer for your needs. Additionally, we will address the advantages and limitations of plastic injection molding, as well as future developments in the industry.
Let’s begin by exploring the basics of what plastic injection molding is and how this process has become a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
What Is Plastic Injection Molding?
Basic Definition
Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce parts by injecting molten plastic material into a mold. This process is widely used in mass production and prototyping of complex plastic parts because it allows for the creation of highly detailed and precise components with a high level of repeatability. The versatility of plastic injection molding makes it applicable across various industries, including automotive, electronics, healthcare, consumer goods, and more.
The basic concept behind plastic injection molding is relatively simple. Plastic material is heated until it reaches a molten state, then injected into a mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies into the shape of the desired part. Once the plastic has hardened, the mold opens, and the finished part is ejected. This process can be repeated many times, making it ideal for high-volume production.
How the Injection Molding Process Works
The injection molding process involves several key steps, each crucial to the production of high-quality plastic parts. Below is a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
- Clamping: The first step in the injection molding process is clamping. The mold consists of two halves, known as the “core” and the “cavity,” which are clamped together by the machine. The clamping unit ensures that the mold halves remain securely closed during the injection process to prevent any material from leaking out.
- Injection: Once the mold is clamped shut, the plastic material is fed into a heated barrel from a hopper. The material is then melted by heating elements within the barrel and mixed by a reciprocating screw. The molten plastic is then injected into the mold cavity through a nozzle and runner system at high pressure.
- Cooling: After the molten plastic fills the mold cavity, it begins to cool and solidify. Cooling is a critical phase because the rate at which the plastic cools affects the final quality of the part. The mold is often equipped with cooling channels that circulate water or oil to regulate the temperature and speed up the cooling process.
- Ejection: Once the plastic has sufficiently cooled and solidified, the mold opens, and the part is ejected by ejector pins or plates. The part may require additional cooling after ejection to ensure it has reached the desired dimensional stability.
- Post-Processing: Depending on the application and material used, the part may undergo post-processing steps such as trimming, assembly, or surface finishing. These steps are often necessary to remove any excess material, enhance the appearance, or prepare the part for use.
Materials Used in Injection Molding
The choice of material is one of the most important decisions in the plastic injection molding process, as it directly impacts the properties and performance of the final part. A wide range of thermoplastics can be used in injection molding, each with its own set of characteristics, advantages, and limitations. Below are some of the most commonly used materials:
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): ABS is a strong, tough material that offers excellent impact resistance and is easy to mold. It is commonly used in automotive parts, consumer electronics, and toys.
- Polypropylene (PP): PP is known for its chemical resistance, flexibility, and durability. It is widely used in automotive components, packaging, and medical devices.
- Nylon (Polyamide): Nylon is a strong, wear-resistant material with good thermal stability. It is often used in automotive applications, electrical connectors, and industrial components.
- Polyethylene (PE): PE is a versatile material with good chemical resistance and flexibility. It is commonly used in packaging, containers, and medical tubing.
- Polycarbonate (PC): PC is a tough, transparent material with high impact resistance. It is used in safety equipment, optical lenses, and electronic housings.
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): PET is known for its strength, rigidity, and clarity. It is widely used in beverage bottles, food containers, and automotive parts.
The selection of material depends on several factors, including the part’s application, mechanical properties, environmental conditions, and cost considerations. Engineers and designers work closely with material suppliers to choose the best material for each specific application.
Types of Plastic Injection Molding Parts
Overview of Different Types of Parts
Plastic injection molding can produce a vast array of parts, ranging from simple components to complex assemblies. The versatility of this manufacturing process allows for the creation of parts with various shapes, sizes, and functionalities. Below is an overview of the different types of parts that can be produced through plastic injection molding:
- Simple Parts: These are straightforward components with basic geometries, such as caps, lids, and fasteners. Simple parts are typically produced in high volumes and require minimal post-processing.
- Complex Parts: These parts feature intricate designs, tight tolerances, and multiple components. Examples include automotive dashboards, electronic housings, and medical devices. Complex parts often require advanced molding techniques, such as overmolding or insert molding.
- Multi-Material Parts: Multi-material injection molding allows for the production of parts made from two or more different materials. This process is used to create parts with enhanced properties, such as improved grip, flexibility, or aesthetics. Examples include toothbrush handles, automotive switches, and seals.
- Thin-Walled Parts: Thin-walled injection molding is used to produce parts with very thin sections, such as packaging containers and disposable medical products. This process requires precise control over the molding parameters to ensure that the material flows evenly and fills the mold cavity without creating defects.
- High-Precision Parts: These parts require extremely tight tolerances and high dimensional accuracy. They are commonly used in applications where precision is critical, such as in aerospace components, optical lenses, and electronic connectors.
Examples of Common Injection Molded Parts
Plastic injection molding is used to produce a wide range of parts across various industries. Here are some common examples:
- Automotive Components: Plastic injection molding is widely used in the automotive industry to produce components such as dashboards, bumpers, grilles, air vents, and interior trim. These parts must meet strict safety and durability standards, making injection molding an ideal manufacturing method.
- Consumer Products: Many everyday items are produced using plastic injection molding, including containers, toys, household appliances, and furniture. The process allows for the efficient production of large volumes of consumer products with consistent quality.
- Medical Devices: Injection molding is used to produce a variety of medical devices and components, such as syringes, surgical instruments, catheters, and drug delivery systems. These parts often require high precision and must comply with strict regulatory standards.
- Electronics: The electronics industry relies heavily on injection molding for the production of housings, connectors, switches, and other components. Injection molding allows for the creation of parts with complex geometries and precise dimensions, which are essential for electronic devices.
Custom vs. Standard Injection Molded Parts
When it comes to plastic injection molding, parts can be categorized as either custom or standard. Understanding the difference between these two categories is important for determining the best approach for your project.
- Custom Injection Molded Parts: Custom parts are designed and produced specifically for a particular application or product. These parts are tailored to meet the unique requirements of the customer, including specific dimensions, material properties, and functionality. Custom injection molding is ideal for projects where unique designs or specialized performance characteristics are required.
- Standard Injection Molded Parts: Standard parts are pre-designed and produced in large quantities for general use. These parts are typically off-the-shelf components that can be used in a wide range of applications. Standard parts are often more cost-effective and readily available, making them a good choice for projects with common requirements.
Choosing between custom and standard parts depends on factors such as the complexity of the design, the intended application, and budget constraints. Custom parts offer greater flexibility and can be optimized for specific needs, while standard parts provide a faster and more cost-effective solution for general applications.
Design Considerations for Injection Molded Parts
Importance of Design in Injection Molding
Design plays a crucial role in the success of plastic injection molding projects. A well-designed part not only meets the functional and aesthetic requirements but also ensures that the manufacturing process is efficient and cost-effective. Design considerations must account for the material properties, molding process, and the intended use of the part.
Poor design choices can lead to a variety of issues, such as defects, increased production costs, and longer cycle times. Therefore, it is essential to work closely with experienced engineers and designers who understand the intricacies of injection molding and can optimize the design for manufacturability.
Key Design Principles
Several key design principles must be considered when creating parts for plastic injection molding. These principles help ensure that the parts are produced with high quality, consistency, and efficiency:
- Wall Thickness: Maintaining uniform wall thickness is one of the most important design principles in injection molding. Variations in wall thickness can lead to defects such as warping, sink marks, and uneven cooling. Uniform walls also promote better material flow and reduce stress concentrations within the part.
- Draft Angles: Draft angles are slight tapers added to the vertical surfaces of the part to facilitate its removal from the mold. Without draft angles, the part may stick to the mold, leading to damage or defects. The appropriate draft angle depends on factors such as material type and part geometry.
- Rib Design: Ribs are structural features that add strength and rigidity to the part without increasing its overall thickness. Proper rib design is essential to avoid issues such as sink marks and warping. Ribs should be designed with adequate thickness and spacing to maintain the part’s structural integrity.
Common Design Challenges
Designing parts for injection molding presents several challenges that must be addressed to ensure a successful outcome. Some common design challenges include:
- Avoiding Defects: Defects such as warping, sink marks, and flash can occur if the part is not designed properly. These defects can result from factors such as uneven cooling, excessive material flow, or improper mold design. Addressing these issues during the design phase can help prevent defects and reduce the need for rework.
- Cooling Efficiency: Efficient cooling is essential to minimize cycle times and ensure consistent part quality. The design of the part, mold, and cooling channels must work together to promote even cooling and reduce the risk of warping or distortion.
- Material Selection: Choosing the right material for the part is critical to achieving the desired performance and appearance. Material selection should take into account factors such as strength, flexibility, chemical resistance, and cost. Additionally, the material’s flow properties and shrinkage rates must be considered during the design process.
Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) is a critical aspect of injection molding that focuses on optimizing the part design to ensure it can be manufactured efficiently and cost-effectively. DFM involves collaboration between designers, engineers, and manufacturers to identify potential issues early in the design process and make necessary adjustments.
Key considerations in DFM include:
- Material Flow: Ensuring that the plastic material flows smoothly through the mold cavity without creating voids, weld lines, or other defects.
- Part Ejection: Designing the part with appropriate draft angles, ejector pin locations, and other features to facilitate easy removal from the mold.
- Tooling Complexity: Simplifying the mold design to reduce tooling costs, maintenance requirements, and production cycle times.
By incorporating DFM principles into the design process, manufacturers can reduce production costs, improve part quality, and shorten lead times.
The Injection Molding Process in Detail
Mold Design and Fabrication
The design and fabrication of the mold are critical steps in the injection molding process. The mold is essentially a negative imprint of the part to be produced, and its design directly impacts the quality, efficiency, and cost of the production process.
Types of Molds
Molds can be classified into several types based on their design and functionality:
- Single-Cavity Molds: These molds produce one part per cycle and are typically used for low to medium-volume production. Single-cavity molds are simpler in design and less expensive to fabricate, but they have lower production efficiency.
- Multi-Cavity Molds: Multi-cavity molds produce multiple identical parts per cycle, increasing production efficiency and reducing per-unit costs. These molds are more complex and expensive to fabricate, but they are ideal for high-volume production.
- Family Molds: Family molds are a type of multi-cavity mold that produces different parts within the same mold. This approach is useful for producing sets of parts that will be assembled together, such as components of a plastic housing.
- Hot Runner Molds: Hot runner molds use a heated manifold to keep the plastic material in a molten state as it flows through the mold. This reduces waste and improves cycle times by eliminating the need to cool and re-melt the material between cycles.
Mold Fabrication
Mold fabrication involves the machining of steel or aluminum blocks to create the cavities and features needed to produce the part. The process requires precision machining techniques, such as CNC milling, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), and grinding, to achieve the desired dimensions and surface finish.
The choice of material for the mold depends on factors such as production volume, part complexity, and budget. Steel molds are durable and can withstand high-volume production, while aluminum molds are less expensive and suitable for low-volume or prototype production.
Molding Cycles
The injection molding cycle is the sequence of events that occur during the production of each part. Understanding the molding cycle is essential for optimizing production efficiency and ensuring consistent part quality.
Explanation of a Typical Molding Cycle
A typical injection molding cycle consists of the following stages:
- Mold Closing: The two halves of the mold (core and cavity) are clamped together by the machine’s clamping unit.
- Injection: Molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity through the nozzle and runner system. The injection phase is completed in a matter of seconds, depending on the part size and complexity.
- Cooling: Once the mold cavity is filled, the plastic begins to cool and solidify. The cooling time is determined by factors such as part thickness, material properties, and mold temperature.
- Mold Opening: After the part has cooled, the mold opens, and the part is ejected by ejector pins or plates.
- Ejection: The finished part is ejected from the mold, and the mold closes again to begin the next cycle.
How Cycle Time Impacts Production Efficiency
Cycle time is a critical factor in the overall efficiency of the injection molding process. A shorter cycle time allows for higher production rates, reducing the cost per part. However, it is important to balance cycle time with part quality. Rushing the process can lead to defects, while overly long cycle times can reduce productivity.
Manufacturers optimize cycle time by adjusting parameters such as injection speed, cooling time, and mold temperature. Advanced process monitoring systems can also help identify opportunities for cycle time reduction without compromising quality.
Injection Molding Machine Settings
The settings on the injection molding machine play a crucial role in determining the quality of the final part. These settings must be carefully calibrated to ensure that the material flows smoothly into the mold, fills the cavity completely, and cools evenly.
Key Parameters
Some of the key parameters that need to be controlled during the injection molding process include:
- Temperature: The temperature of the material, mold, and machine barrel must be carefully controlled to ensure proper melting, flow, and cooling of the plastic. Each material has its own optimal temperature range, which must be maintained throughout the process.
- Pressure: Injection pressure is the force used to push the molten plastic into the mold cavity. Proper pressure ensures that the material fills the cavity completely and conforms to the mold’s features. Excessive pressure can lead to defects, while insufficient pressure may result in incomplete parts.
- Injection Speed: The speed at which the molten plastic is injected into the mold affects the material flow and cooling. Faster injection speeds can reduce cycle times, but they also increase the risk of defects such as flow lines or weld lines.
- Cooling Time: The cooling time is the duration for which the part remains in the mold after injection. Proper cooling is essential to achieve the desired dimensional stability and surface finish. Insufficient cooling can lead to warping, while excessive cooling increases cycle time.
Quality Control in Injection Molding
Quality control is a critical aspect of the injection molding process, ensuring that each part meets the required specifications and standards. Quality control involves both in-process monitoring and post-molding inspection.
In-Process Quality Checks
In-process quality checks are conducted during the injection molding cycle to monitor parameters such as temperature, pressure, and material flow. These checks help detect and address any issues that arise during production, preventing defects and reducing scrap rates.
Common in-process quality control techniques include:
- Dimensional Accuracy Checks: Measurements are taken to ensure that the part dimensions match the design specifications. This can be done using tools such as calipers, micrometers, or coordinate measuring machines (CMM).
- Visual Inspection: Parts are inspected visually for defects such as warping, sink marks, flash, or surface imperfections. Visual inspection can be done manually or using automated vision systems.
Post-Molding Processes
After the parts are ejected from the mold, they may undergo post-molding processes to achieve the desired final quality. These processes can include:
- Trimming and Deburring: Excess material, known as flash, is removed from the part using cutting tools, knives, or lasers. Deburring smooths out rough edges to improve the part’s appearance and functionality.
- Surface Finishing: Parts may require additional surface finishing to enhance their appearance or functionality. This can include processes such as painting, plating, or applying textures to the surface.
- Assembly: In some cases, multiple injection-molded parts are assembled together to create a final product. This can involve joining processes such as welding, gluing, or fastening.
By implementing rigorous quality control measures and post-molding processes, manufacturers can ensure that each part meets the required specifications and performs as expected in its intended application.
Applications of Plastic Injection Molding Parts
Industry-Specific Applications
Plastic injection molding is used across a wide range of industries, each with its own specific requirements and applications. Here are some of the key industries that rely on plastic injection molding:
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is one of the largest users of plastic injection molding. Injection-molded parts are used in a wide variety of applications within vehicles, including interior components such as dashboards, door panels, and air vents, as well as exterior parts like bumpers, grilles, and mirror housings. Under-the-hood components such as engine covers, fluid reservoirs, and air intake manifolds are also commonly produced using injection molding.
The use of plastic injection molding in the automotive industry offers several advantages, including weight reduction, cost savings, and design flexibility. Plastic parts can be produced with complex geometries and integrated features, which helps reduce the number of components and assembly steps in a vehicle.
Electronics
The electronics industry relies heavily on injection molding for the production of housings, connectors, switches, and other components. Injection molding allows for the creation of parts with precise dimensions and intricate details, which are essential for the functionality and reliability of electronic devices.
Examples of injection-molded parts in the electronics industry include smartphone cases, laptop shells, connector housings, and switch components. The use of high-performance plastics with good electrical insulation properties and thermal stability is critical in these applications.
Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, plastic injection molding is used to produce a wide range of medical devices and components, including syringes, surgical instruments, catheters, and drug delivery systems. These parts often require high precision, biocompatibility, and compliance with strict regulatory standards.
Injection molding allows for the production of medical parts with complex geometries and tight tolerances, which are essential for ensuring patient safety and effective treatment. Additionally, the process can be used to produce single-use disposable medical devices, which are critical for maintaining hygiene and preventing cross-contamination.
Consumer Goods
Plastic injection molding is widely used in the production of consumer goods, including household appliances, kitchenware, furniture, toys, and packaging. The process allows for the efficient production of large volumes of consumer products with consistent quality and a wide range of design options.
Examples of injection-molded consumer goods include food containers, plastic chairs, storage bins, and toy components. Injection molding enables the production of parts with various colors, textures, and finishes, allowing manufacturers to create aesthetically appealing and functional products.
Innovations in Injection Molding
The field of plastic injection molding is continuously evolving, with new technologies and innovations driving improvements in efficiency, quality, and sustainability. Some of the key innovations in injection molding include:
Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies into injection molding is transforming the manufacturing process. Smart manufacturing systems use sensors, data analytics, and machine learning to monitor and optimize the injection molding process in real-time. This allows manufacturers to detect and address issues early, reduce waste, and improve overall efficiency.
3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
While injection molding remains the dominant method for producing plastic parts in large volumes, 3D printing and additive manufacturing are gaining traction as complementary technologies. 3D printing allows for rapid prototyping and small-batch production of complex parts, providing greater flexibility and faster turnaround times.
In some cases, 3D printing is used to create molds or mold inserts, enabling the production of custom injection-molded parts without the need for expensive tooling.
Case Studies
To illustrate the versatility and impact of plastic injection molding, let’s explore a few case studies of successful projects in different industries:
Automotive Case Study: Lightweight Dashboard
A leading automotive manufacturer sought to reduce the weight of its vehicles to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. The company turned to plastic injection molding to produce a lightweight dashboard assembly. By using a high-strength polymer and optimizing the part design for weight reduction, the manufacturer was able to achieve a significant reduction in weight without compromising safety or durability. The new dashboard also featured integrated air vents and mounting points, reducing the number of separate components and simplifying assembly.
Electronics Case Study: Smartphone Housing
A consumer electronics company needed to produce a durable and aesthetically pleasing housing for its latest smartphone model. The housing required a combination of rigidity, impact resistance, and a smooth surface finish. The company selected a polycarbonate material for its excellent mechanical properties and used a multi-cavity mold to achieve high production efficiency. The injection molding process allowed for the precise replication of the intricate design features, including button recesses and camera openings. The final product met the company’s quality standards and was successfully launched to the market.
Healthcare Case Study: Disposable Syringes
A medical device manufacturer needed to produce large quantities of disposable syringes for use in healthcare settings. The syringes required high precision and compliance with regulatory standards for medical devices. The company used injection molding to produce the syringe barrels and plungers from a medical-grade polypropylene material. The process allowed for the consistent production of syringes with tight tolerances and a smooth finish, ensuring reliable performance and patient safety. The manufacturer also implemented automated assembly and packaging systems to streamline production and meet the high demand.
These case studies demonstrate the wide range of applications for plastic injection molding and the benefits it offers in terms of design flexibility, production efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Advantages of Plastic Injection Molding
Efficiency and Scalability
One of the primary advantages of plastic injection molding is its efficiency and scalability. The process is well-suited for high-volume production, allowing manufacturers to produce large quantities of parts quickly and consistently. Once the mold is designed and fabricated, the injection molding process can be repeated with minimal variation between parts.
Injection molding machines are capable of producing thousands or even millions of parts in a relatively short period, making it an ideal method for mass production. The ability to produce parts at scale also contributes to cost savings, as the per-unit cost decreases with higher production volumes.
Cost-Effectiveness
Plastic injection molding is a cost-effective manufacturing method, particularly for large production runs. The initial investment in mold design and fabrication can be significant, but this cost is offset by the low per-unit cost of production. As production volumes increase, the cost per part continues to decrease, making injection molding an economical choice for high-volume manufacturing.
In addition to cost savings through scale, injection molding allows for material optimization, reducing waste and lowering material costs. The process also enables the production of complex parts in a single step, eliminating the need for additional assembly or finishing processes.
Material Versatility
Plastic injection molding offers a high degree of material versatility, allowing manufacturers to choose from a wide range of thermoplastics to meet the specific requirements of their application. Whether the part needs to be strong, flexible, transparent, or resistant to chemicals, there is a material available that can achieve the desired properties.
This versatility extends to multi-material injection molding, where two or more materials are combined to create a single part with enhanced characteristics. For example, a part can be produced with a rigid core for strength and a soft outer layer for improved grip and comfort.
Consistency and Precision
Injection molding is known for its ability to produce parts with high consistency and precision. The process allows for tight tolerances and accurate replication of complex geometries, ensuring that each part meets the required specifications. This level of precision is critical in industries such as automotive, electronics, and healthcare, where even minor deviations can impact the performance or safety of the product.
The consistency achieved through injection molding also contributes to quality control, as parts produced in different batches or even different facilities can be virtually identical. This is particularly important for global manufacturing operations, where consistency across locations is essential.
Disadvantages and Limitations of Plastic Injection Molding
Initial Costs and Investment
One of the main disadvantages of plastic injection molding is the high initial cost associated with mold design and fabrication. Molds are custom-made for each part, and the cost can vary depending on factors such as the complexity of the design, the number of cavities, and the material used for the mold.
For small-batch production or prototypes, the high upfront cost of injection molding may not be justifiable. In such cases, alternative manufacturing methods, such as 3D printing or CNC machining, may be more cost-effective.
Design Limitations
While plastic injection molding offers significant design flexibility, there are certain limitations that must be considered. For example, the process is not well-suited for producing parts with extremely thin walls or very large dimensions. These limitations are due to factors such as material flow, cooling, and the mechanical properties of the plastic.
Additionally, some designs may require complex tooling or multiple molds, which can increase the cost and lead time of the project. Designers must work closely with engineers to ensure that the part design is compatible with the injection molding process and can be produced efficiently.
Environmental Considerations
The environmental impact of plastic injection molding is a growing concern, particularly in terms of waste generation and energy consumption. The process generates waste in the form of excess material, known as flash, as well as sprues and runners that must be removed and discarded or recycled.
Energy consumption is another environmental consideration, as injection molding machines require significant amounts of energy to heat the plastic material and power the hydraulic or electric systems. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting energy-efficient machines and practices to reduce their environmental footprint.
Recycling of plastic waste is also a challenge, as not all materials can be easily recycled. However, advances in recycling technology and the development of biodegradable plastics are helping to address these concerns and make injection molding more sustainable.
The Future of Plastic Injection Molding
Trends and Developments
The future of plastic injection molding is being shaped by several key trends and developments that are driving innovation and improving the efficiency and sustainability of the process.
Growth of Bioplastics and Sustainable Materials
As environmental concerns continue to rise, there is growing interest in bioplastics and other sustainable materials for injection molding. Bioplastics are made from renewable sources, such as corn starch or sugarcane, and offer the potential for reduced environmental impact compared to traditional petroleum-based plastics.
In addition to bioplastics, manufacturers are exploring the use of recycled materials in injection molding. Recycled plastics can be used to produce high-quality parts, reducing the demand for virgin materials and minimizing waste.
Advances in Mold Technology and Automation
Advances in mold technology and automation are improving the efficiency and precision of the injection molding process. For example, the use of conformal cooling channels in molds allows for more efficient heat transfer and faster cooling times, reducing cycle times and improving part quality.
Automation is also playing a significant role in the future of injection molding. Automated systems can handle tasks such as material handling, part ejection, and quality inspection, reducing labor costs and increasing production efficiency.
Challenges and Opportunities
While plastic injection molding offers many benefits, the industry also faces challenges that must be addressed to ensure continued growth and success.
Addressing Environmental Concerns
The environmental impact of plastic injection molding is a significant challenge that the industry must address. This includes reducing waste, improving energy efficiency, and finding sustainable alternatives to traditional plastics. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting green manufacturing practices and exploring new materials to meet these challenges.
Opportunities for Innovation and New Applications
Despite the challenges, there are numerous opportunities for innovation in plastic injection molding. The development of new materials, such as high-performance polymers and composites, is expanding the range of applications for injection-molded parts. Additionally, advances in digital manufacturing and additive technologies are opening up new possibilities for custom and small-batch production.
The Role of Digital Manufacturing
Digital manufacturing is playing an increasingly important role in the future of plastic injection molding. Technologies such as 3D printing, computer-aided design (CAD), and simulation software are enabling more efficient and flexible production processes.
For example, 3D printing can be used to create prototypes and mold inserts, allowing for rapid design iteration and reducing the time and cost of mold fabrication. Simulation software allows manufacturers to predict and optimize the injection molding process, improving part quality and reducing the risk of defects.
Choosing the Right Injection Molding Partner
What to Look for in a Plastic Parts Manufacturer
Choosing the right plastic parts manufacturer is a critical decision that can impact the success of your project. When selecting a manufacturer, consider the following key criteria:
- Experience and Expertise: Look for a manufacturer with a proven track record in producing high-quality injection-molded parts for your specific industry. Experience in handling similar projects is a good indicator of their capability to meet your requirements.
- Technical Capabilities: Ensure that the manufacturer has the necessary equipment, technology, and expertise to produce your parts to the required specifications. This includes the ability to work with your chosen materials and meet your desired production volumes.
- Quality Control: A strong quality control process is essential for ensuring that your parts meet the required standards. Ask about the manufacturer’s quality control procedures and certifications, such as ISO 9001 or ISO 13485.
- Production Capacity: Consider the manufacturer’s production capacity and lead times to ensure that they can meet your deadlines and scale production as needed.
Questions to Ask Potential Manufacturers
When evaluating potential manufacturers, it’s important to ask the right questions to ensure that they are the right fit for your project. Some questions to consider include:
- What materials do you specialize in?
- Can you provide case studies or examples of similar projects you have completed?
- What is your approach to quality control, and what certifications do you hold?
- What are your typical lead times, and how do you handle rush orders?
- What is your process for managing changes or modifications to the design?
Evaluating Costs and Production Capabilities
When choosing a plastic parts manufacturer, it’s important to evaluate both the costs and production capabilities to ensure that they can meet your needs within your budget. Consider factors such as:
- Tooling Costs: The cost of mold design and fabrication can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the part. Make sure to get a detailed quote that includes all associated costs.
- Per-Unit Costs: Ask for a breakdown of the per-unit costs, including material, labor, and overhead. Compare these costs across different manufacturers to ensure that you are getting a competitive price.
- Production Capacity: Ensure that the manufacturer has the capacity to meet your required production volumes, both for the initial order and any future scaling needs.
- Lead Times: Consider the manufacturer’s lead times and their ability to meet your project deadlines. Ask about their process for handling delays or unexpected issues.
Case Studies of Successful Partnerships
Successful partnerships with plastic parts manufacturers can lead to long-term relationships and ongoing collaboration. Here are a few examples of successful partnerships:
Automotive Partnership: Tier 1 Supplier Collaboration
An automotive OEM partnered with a Tier 1 supplier specializing in plastic injection molding to develop a new line of interior components. The partnership involved close collaboration between the design and engineering teams to optimize the parts for manufacturability. The supplier’s expertise in material selection and mold design allowed for the production of lightweight, durable components that met the OEM’s performance and cost targets. The partnership resulted in a successful product launch and continued collaboration on future projects.
Healthcare Partnership: Medical Device Development
A medical device company partnered with a plastic injection molding manufacturer to develop a new drug delivery system. The project required high precision, biocompatibility, and compliance with regulatory standards. The manufacturer worked closely with the company’s R\&D team to select the appropriate materials and optimize the design for injection molding. The partnership led to the successful development and approval of the device, with the manufacturer continuing to produce the components for commercial use.
These case studies demonstrate the importance of selecting the right injection molding partner and the value of collaboration in achieving successful outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Common Questions About Injection Molding
Here are some common questions about plastic injection molding and their answers:
- What is the typical lead time for injection molded parts? Lead times can vary depending on the complexity of the part, the material used, and the production volume. On average, lead times range from 4 to 12 weeks, but they can be longer for more complex projects.
- How do I choose the right material for my parts? Material selection depends on factors such as the part’s intended use, required mechanical properties, environmental conditions, and cost. Working with an experienced manufacturer can help you select the best material for your application.
- What are the most common defects in injection molding and how are they prevented? Common defects include warping, sink marks, flash, and voids. These defects can be prevented through careful design, proper mold maintenance, and precise control of the injection molding parameters.
Practical Tips for Newcomers
For businesses new to injection molding, here are some practical tips:
- Start with Prototyping: Before committing to full-scale production, consider creating prototypes to test and refine your design. This can help identify potential issues early and reduce the risk of costly rework.
- Collaborate with Experts: Work closely with experienced designers, engineers, and manufacturers to optimize your part design for injection molding. Their expertise can help you achieve better results and avoid common pitfalls.
- Invest in Quality: While it may be tempting to cut costs, investing in high-quality materials, molds, and processes will pay off in the long run by reducing defects, improving part performance, and increasing customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points
Plastic injection molding is a versatile and efficient manufacturing process that plays a critical role in producing parts for a wide range of industries. Understanding the process, design considerations, and material options is essential for achieving successful outcomes in injection molding projects.
Final Thoughts
By selecting the right plastic parts manufacturer and investing in quality design and materials, businesses can take full advantage of the benefits of injection molding. Whether you are producing high-volume consumer goods or precision medical devices, injection molding offers the flexibility and scalability needed to meet your production goals.
Call to Action
If you are considering plastic injection molding for your next project, we encourage you to reach out to an experienced plastic parts manufacturer. Their expertise can help you navigate the complexities of the process and ensure that your parts are produced to the highest standards.
Additional Resources
Links to Further Reading
For more information on plastic injection molding, consider exploring the following resources:
- The Basics of Plastic Injection Molding: An Introduction
- Designing for Injection Molding: Best Practices and Tips
- Advanced Materials for Injection Molding: What You Need to Know
Glossary of Terms
Here are some key terms related to plastic injection molding:
- Injection Molding: A manufacturing process that involves injecting molten plastic into a mold to produce parts.
- Mold: A custom-made tool used to shape the plastic material into the desired part.
- Cycle Time: The time required to complete one injection molding cycle, including mold closing, injection, cooling, and ejection.
- Flash: Excess material that forms around the edges of a part during molding and must be trimmed off.
- Bioplastics: Plastics made from renewable sources, such as corn starch or sugarcane, that offer reduced environmental impact.
Contact Information
If you have any questions or would like to discuss your injection molding project, please feel free to contact us at [contact information]. We are here to help you achieve your manufacturing goals and bring your products to life.