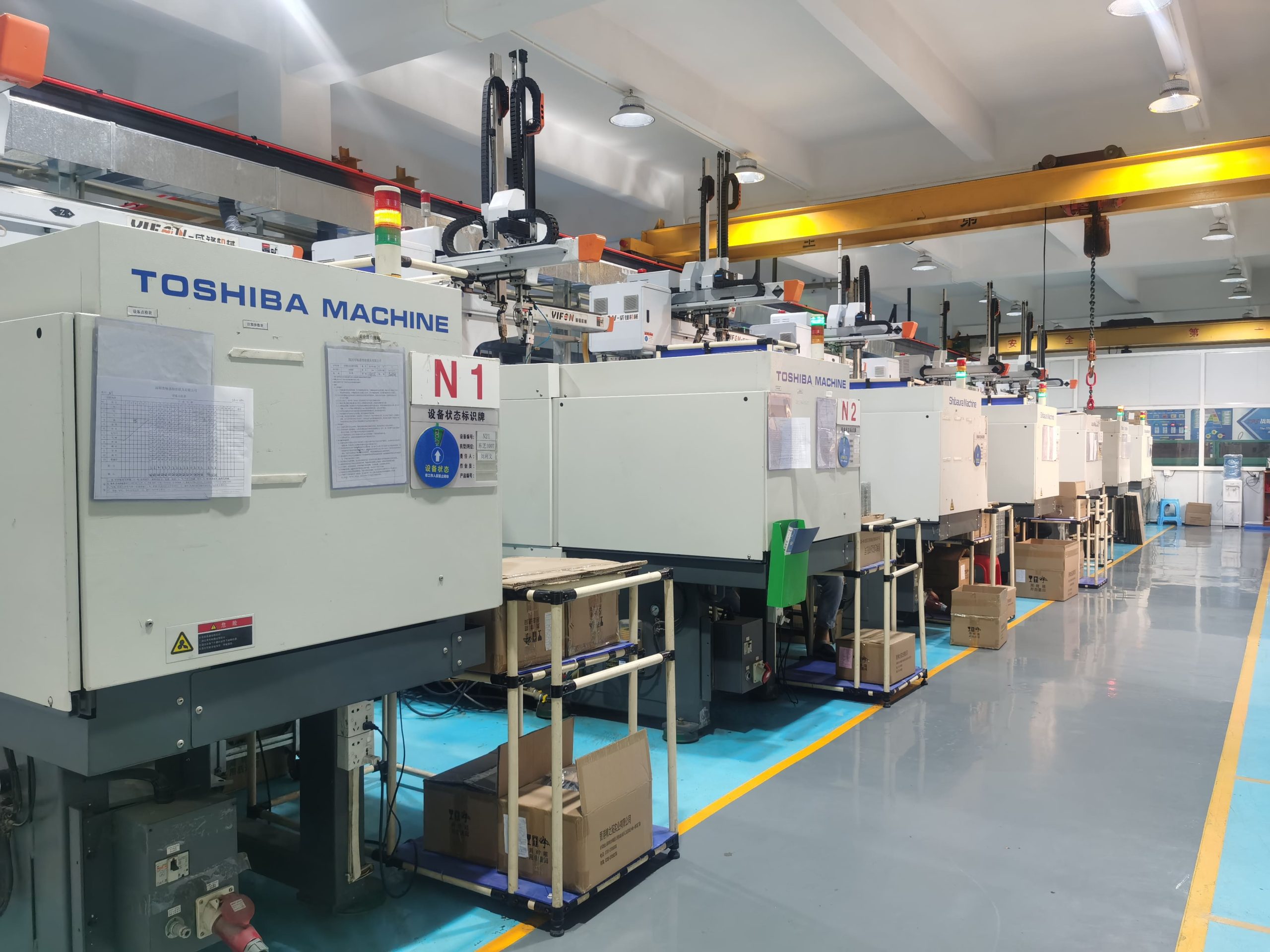
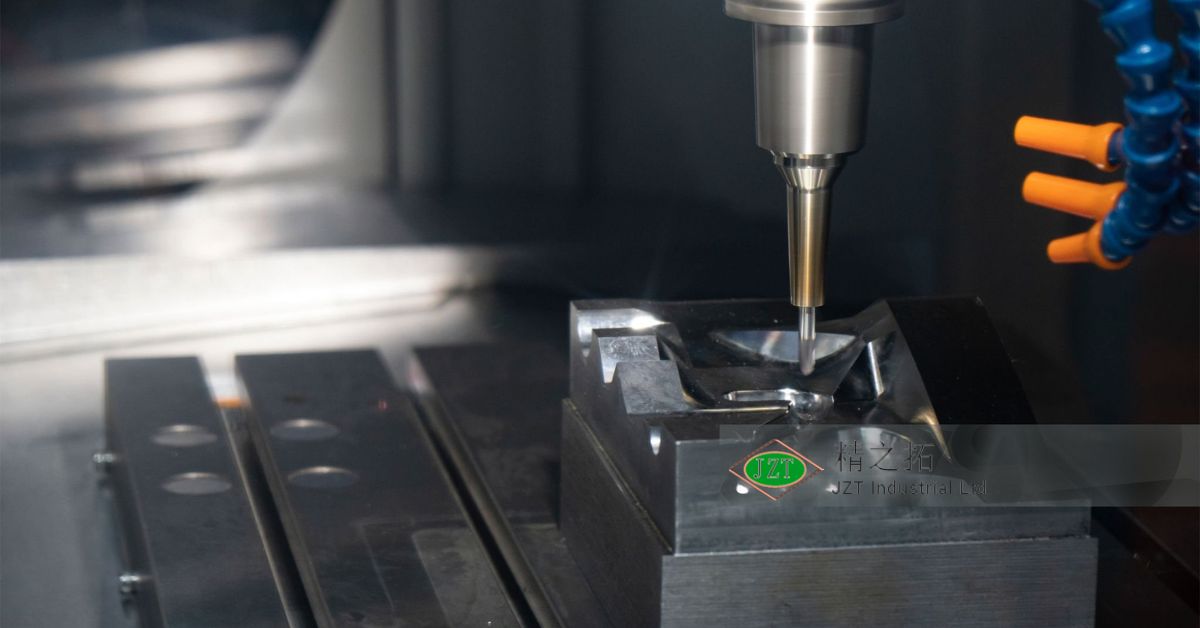
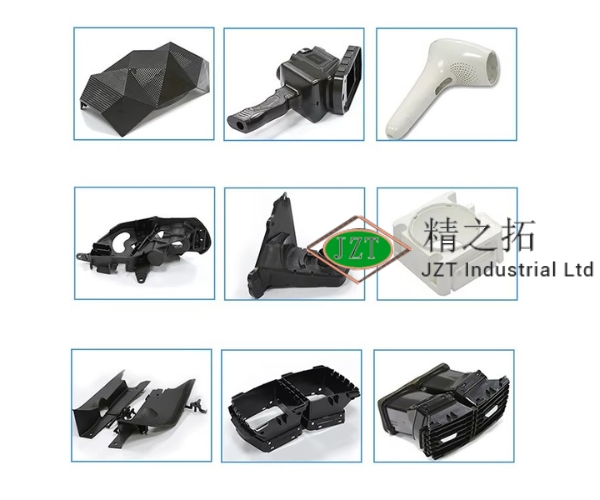
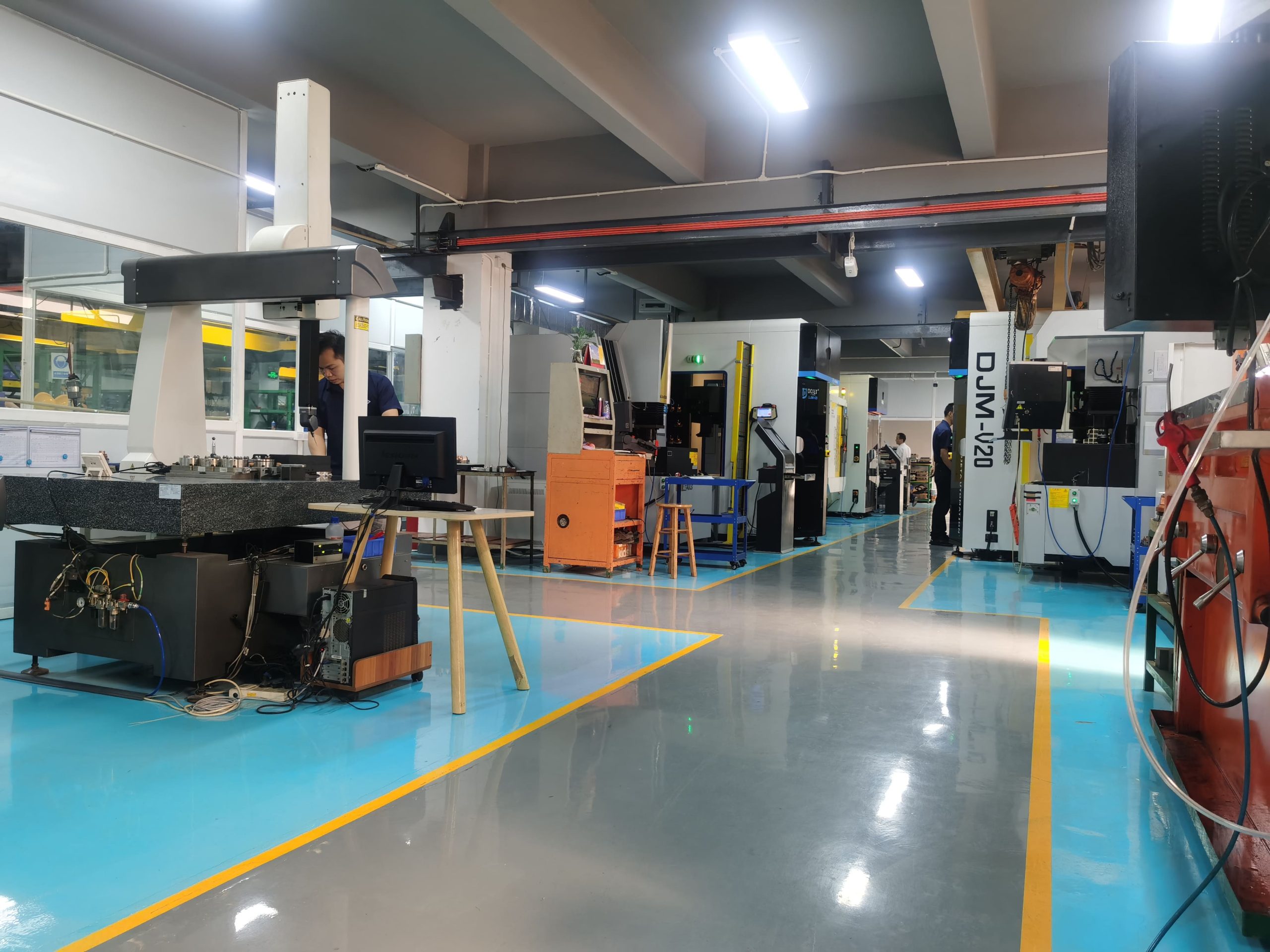
Introduction
The automotive industry relies heavily on precision and efficiency, especially when it comes to producing high-quality components that are safe, durable, and reliable. Within this sector, the automotive aftermarket is a significant area, supplying consumers with parts for replacement, repair, and customization. The aftermarket industry includes everything from bumpers and grilles to custom interior parts, allowing consumers to maintain, repair, and even personalize their vehicles according to their needs.
One manufacturing process that has proven essential in the automotive aftermarket is plastic injection molding. Injection molding enables the high-speed production of parts that meet stringent quality requirements and withstand the demands of daily use. It offers the flexibility to create both standard and custom plastic parts with precision and efficiency, making it a preferred choice for plastic parts manufacturers serving the aftermarket. In this article, we will delve into why injection molding is crucial for automotive aftermarket parts, exploring its benefits, material choices, design flexibility, and more.
Understanding Injection Molding and Its Relevance to Automotive Parts
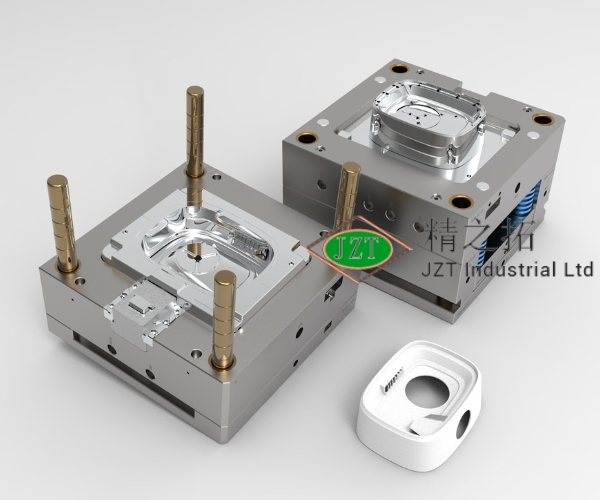
Injection molding is a manufacturing process that shapes molten plastic into precise parts by injecting it into a pre-designed mold. This method is highly valued in the automotive industry for its ability to produce complex shapes quickly and with remarkable accuracy. Plastic injection molding for the automotive aftermarket enables manufacturers to create parts that fit seamlessly into existing assemblies, meet safety standards, and fulfill consumer demand for durable replacement and custom parts.
What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding begins by heating plastic pellets until they melt. This molten plastic is then injected under high pressure into a mold cavity shaped according to the desired part. After cooling and solidifying, the part is ejected from the mold, ready for finishing and assembly. This process can produce parts with intricate details, complex geometries, and exact specifications, which are essential for the tight tolerances required in automotive applications. Injection molding’s precision, scalability, and efficiency make it a cornerstone of plastic parts manufacturing, especially in industries requiring large volumes and high-quality standards.
Benefits of Injection Molding for Automotive Parts
Injection molding offers several advantages that make it ideal for automotive parts production. First, it allows for mass production with minimal per-part costs, making it highly cost-effective for large volumes of identical parts. Second, it ensures dimensional accuracy, which is critical in the automotive industry where parts must fit precisely into assemblies. Additionally, injection molding allows for material flexibility, enabling manufacturers to select from a wide range of plastics and composites, each suited to specific performance requirements such as impact resistance, heat tolerance, and lightweighting.
How Injection Molding Fits the Requirements of Aftermarket Parts
The automotive aftermarket is distinct from OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) production in that it offers parts for repair, replacement, and customization rather than initial assembly. Injection molding is well-suited to meet these unique demands. It allows for the production of parts in smaller batches for specialized markets, like customization enthusiasts, as well as high-volume production for widely used replacement parts. The custom plastic parts that can be manufactured with injection molding range from complex interior pieces to functional engine components, meeting both aesthetic and functional needs in the aftermarket sector.
The Automotive Aftermarket Industry: An Overview
The automotive aftermarket industry is a vast market that includes all vehicle parts, equipment, and accessories sold after the vehicle’s initial sale. Consumers rely on aftermarket parts for maintenance, repairs, and upgrades, making it an essential sector for vehicle longevity and customization. This industry is experiencing significant growth due to increased vehicle ownership, longer vehicle lifespans, and consumer interest in personalizing their cars.
Definition and Scope of the Aftermarket Industry
The aftermarket industry encompasses all parts sold and installed after the original sale of a vehicle, including items like replacement parts, performance upgrades, and decorative accessories. These parts are designed to replace or enhance OEM components, and they play a crucial role in ensuring vehicles remain operational, safe, and up-to-date with consumer preferences. Aftermarket parts range from basic items like air filters and brake pads to more specialized components such as bumpers, spoilers, and engine covers, many of which are produced through plastic injection molding.
Market Demand and Trends
The aftermarket industry is driven by a range of trends, including the DIY repair movement, the rise of online retail, and a growing interest in vehicle customization. Consumers are increasingly inclined to perform their own repairs or enhance their vehicles with personalized parts, such as custom interior trims or exterior upgrades. Additionally, the aftermarket sector has benefited from advancements in plastic injection molds, which allow for a broader variety of parts that meet both aesthetic and functional demands.
Importance of Quality and Cost in Aftermarket Parts
Quality and affordability are critical in the aftermarket industry. Consumers expect aftermarket parts to perform as well as or better than OEM parts at a competitive price point. This balance of quality and cost-efficiency is essential for plastic parts manufacturers, who rely on injection molding to meet these demands without sacrificing durability or safety. Ensuring that each part meets high standards is essential, especially for components that impact a vehicle’s safety, such as bumper reinforcements or airbag housings.
Challenges in the Aftermarket Sector
Manufacturers in the aftermarket sector face several challenges, including meeting the stringent quality standards set by OEMs, maintaining cost control, and ensuring fast production times to meet high demand. The use of injection molding helps address these challenges, offering manufacturers a reliable method for producing high-quality parts at scale, with consistency, and at a price point that is competitive within the aftermarket industry.
Key Advantages of Injection Molding for Automotive Aftermarket Parts
Injection molding provides numerous benefits that are particularly valuable in the production of aftermarket automotive parts. From cost-effectiveness to design flexibility, this manufacturing method enables aftermarket parts to be produced to high standards while meeting the specific demands of consumers.
1. Cost-Effective Production for High-Volume Needs
One of the major advantages of injection molding is its ability to produce parts in high volumes at a low per-unit cost. After the initial investment in plastic injection molds, the cost of each subsequent part decreases significantly, making it ideal for aftermarket manufacturers who need to produce large numbers of parts without escalating costs. This cost-efficiency is particularly beneficial for replacement parts, where maintaining affordability without compromising quality is critical.
2. Precision and Consistency
Precision is paramount in automotive parts, where even minor deviations can affect the fit and function of a component. Injection molding delivers consistent, repeatable accuracy for each part produced, ensuring that every piece meets specified tolerances and integrates seamlessly into the vehicle’s existing assembly. For example, dashboard components, air vents, and trim pieces must fit precisely within the interior structure, a level of precision that injection molding readily achieves.
3. Material Versatility
Injection molding allows for a wide variety of materials, from general-purpose plastics like ABS and polypropylene to high-performance options such as glass-filled nylon. This versatility enables manufacturers to select materials tailored to each part’s functional requirements, whether that means impact resistance for bumpers or heat tolerance for engine covers. Additionally, many plastic parts manufacturers are now incorporating recycled materials, aligning with sustainability goals without compromising the durability of the part.
4. Design Flexibility
Injection molding’s flexibility enables the production of parts with complex geometries, multiple textures, and integrated features. This flexibility is valuable for custom automotive parts, where unique shapes and custom finishes are often requested. Features like clips, holes, and mounts can be molded directly into the part, reducing the need for secondary operations and streamlining the production process. This design flexibility helps meet the diverse and sometimes highly specific requirements of the automotive aftermarket sector.
5. Fast Production Cycles
Injection molding is known for its quick cycle times, which allow for rapid production of parts once the molds are ready. Short cycle times are essential in the aftermarket industry, where there is often a high demand for quick turnaround on replacement parts. By producing parts rapidly, injection molding ensures that aftermarket manufacturers can meet consumer demands efficiently, minimizing lead times and helping retailers keep popular items in stock.
Injection Molding Materials for Automotive Aftermarket Parts
Material selection is a critical aspect of manufacturing automotive parts, as each component has unique performance requirements based on its application. The plastic parts manufacturers serving the aftermarket industry often rely on a selection of durable, high-quality plastics that meet specific criteria for impact resistance, heat tolerance, and flexibility.
Popular Materials Used in Automotive Injection Molding
Several materials are commonly used for automotive injection-molded parts:
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Known for its impact resistance and ability to withstand varying temperatures, ABS is frequently used for interior and exterior parts such as dashboards, trim pieces, and bumper components.
- Polypropylene (PP): Lightweight, flexible, and resistant to chemicals, polypropylene is ideal for parts like door panels, consoles, and other interior elements that require resilience without significant weight.
- Glass-Filled Nylon: Glass-filled nylon provides high strength and heat resistance, making it suitable for parts that need to withstand mechanical stress, such as engine covers, air intake manifolds, and other under-the-hood components.
Material Selection Based on Part Requirements
Each automotive part has specific requirements based on its function and placement within the vehicle. For instance, exterior parts exposed to the elements must be UV-resistant and weatherproof, while engine components require materials that can tolerate high temperatures and mechanical stress. Injection molding enables manufacturers to choose the optimal material for each part’s application, ensuring durability and performance.
Recycled and Sustainable Materials
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in the automotive industry, and many manufacturers are now using recycled materials in aftermarket parts. Recycled polypropylene and other eco-friendly materials are being integrated into parts like bumper fascias and interior trims, supporting environmentally conscious manufacturing without sacrificing quality. This shift not only aligns with industry regulations but also meets consumer demand for sustainable products.
Types of Automotive Aftermarket Parts Manufactured with Injection Molding
Injection molding enables the production of a wide range of automotive aftermarket parts that serve both functional and aesthetic purposes. From interior components that enhance the vehicle’s look to exterior parts that improve safety and performance, injection molding is essential for creating parts that meet diverse aftermarket needs.
Interior Components
Interior components are some of the most commonly injection-molded parts in the aftermarket industry. These include dashboard trims, air vents, cup holders, door panels, and various aesthetic finishes for customization. Interior components must have a high-quality surface finish, as they are visible to and frequently touched by passengers. The injection molding process ensures that these parts meet strict aesthetic standards with smooth surfaces, customizable textures, and color consistency. Custom plastic parts such as color-matched trim and personalized accents are highly sought after in the aftermarket, allowing vehicle owners to personalize their car interiors easily.
Exterior Components
Exterior components such as bumpers, fenders, grilles, and mirror housings are also produced through injection molding. These parts need to be durable and able to withstand environmental factors, including UV exposure, extreme temperatures, and impacts from road debris. Injection molding provides the necessary robustness and resilience, making it ideal for producing parts that can endure these external challenges. Additionally, aftermarket consumers often seek customized exterior parts for aesthetic purposes, such as grilles with unique designs or color-matched bumpers. Injection molding’s precision and versatility enable manufacturers to meet these customization needs effectively.
Functional and Structural Parts
Functional and structural parts, such as engine covers, brackets, and air intake manifolds, play a critical role in vehicle operation and safety. These components are often located in areas that require high durability, thermal resistance, and strength. For example, engine covers must be heat-resistant and capable of withstanding the mechanical stresses of engine vibrations. Using materials like glass-filled nylon and polypropylene, injection molding can produce high-strength parts that meet these rigorous demands. The aftermarket industry relies on injection molding to supply affordable yet durable replacements for these essential parts, ensuring that vehicles continue to perform safely and reliably.
Custom and Performance Upgrades
Automotive enthusiasts frequently turn to the aftermarket sector for custom and performance upgrades. These may include specialized parts such as custom grilles, spoilers, side skirts, and body kits that enhance the vehicle’s appearance and aerodynamics. Injection molding enables the creation of unique designs that cater to personal tastes, with options for custom colors, textures, and even lightweight materials for improved performance. By using injection molding, manufacturers can quickly respond to trends and offer products that allow consumers to personalize and upgrade their vehicles to reflect their preferences.
Replacement Parts
The aftermarket industry provides essential replacement parts that meet or exceed OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) standards, helping consumers maintain their vehicles’ integrity and appearance. Replacement parts such as clips, fasteners, trim pieces, and panel covers are frequently injection molded for consistency, durability, and affordability. These parts are essential for repair shops and DIY enthusiasts alike, providing affordable options for maintaining or restoring vehicles. Injection molding allows manufacturers to replicate the original part specifications closely, ensuring compatibility with existing vehicle assemblies and upholding quality.
The Role of Injection Molding in Ensuring Quality and Durability in Aftermarket Parts
Quality and durability are paramount for automotive parts, particularly those in the aftermarket sector, where parts must match or exceed OEM quality. Injection molding is instrumental in meeting these quality standards, as it ensures precision, consistency, and strength in each part produced.
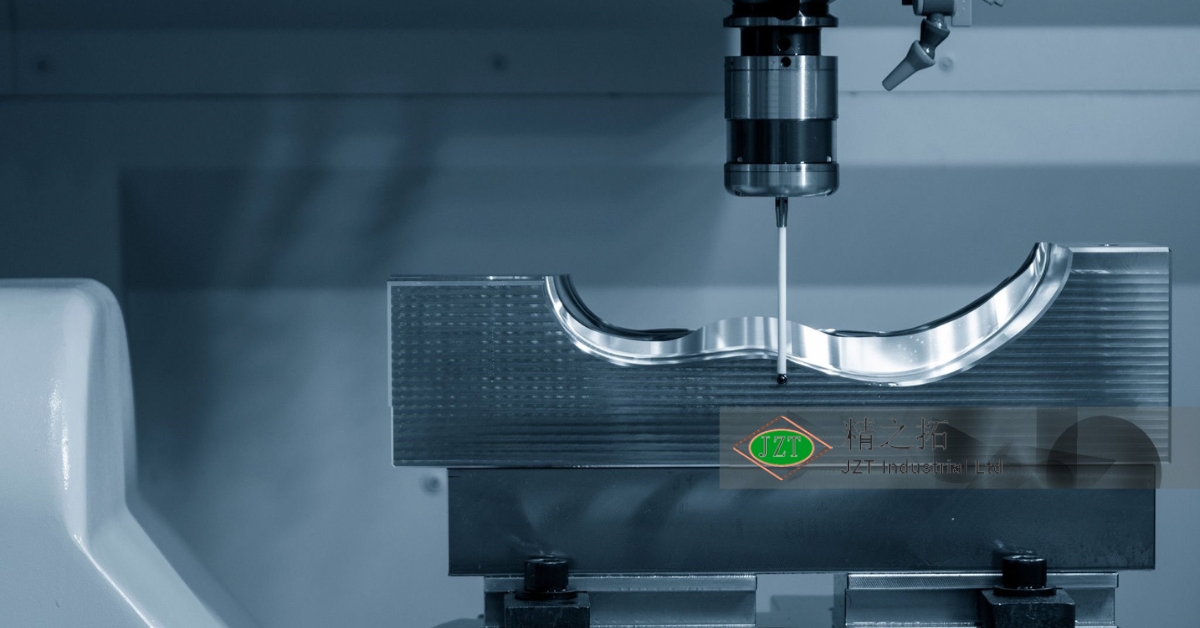
Precision and Accuracy
Injection molding offers the precision needed to create aftermarket parts that fit perfectly within existing assemblies. Accurate dimensions are critical in automotive parts, as slight discrepancies can lead to rattling, misalignment, or functional failures. Injection molding achieves the tight tolerances required to ensure each part integrates seamlessly into the vehicle. This precision is particularly valuable in parts such as interior trims, clips, and brackets that must fit precisely to function correctly and maintain the vehicle’s aesthetic integrity.
Surface Finish and Appearance
The surface finish of injection-molded parts is another key factor in quality. Interior components, for instance, require smooth finishes without imperfections, as they are highly visible and impact the overall aesthetics of the vehicle’s cabin. Injection molding can produce parts with different textures and finishes, whether matte, glossy, or textured, allowing manufacturers to deliver parts that meet specific aesthetic criteria. This capability is also beneficial for custom parts, where unique finishes add to the product’s appeal in the aftermarket.
Durability and Mechanical Strength
Durability is essential for automotive parts, especially those exposed to harsh conditions, like bumpers and engine covers. Injection molding allows for the use of materials with high impact resistance, thermal stability, and UV resistance, ensuring parts can withstand environmental exposure and mechanical stress. This durability is critical for safety-related components and for maintaining the vehicle’s appearance over time. Injection-molded parts retain their structural integrity and appearance even after prolonged use, making them a reliable choice in the aftermarket.
Maintaining Consistency in Large Production Runs
For the aftermarket sector, consistency across large production runs is essential, as parts need to meet the same quality standards repeatedly. Injection molding is highly repeatable, meaning every part produced in a run will have identical dimensions, strength, and finish. This consistency is crucial for ensuring that each aftermarket part functions as expected and matches consumer expectations. By maintaining uniformity, injection molding reduces the likelihood of defects, ensuring reliable performance and minimizing returns or warranty claims.
Challenges of Injection Molding for Automotive Aftermarket Parts and How They Are Addressed
While injection molding provides numerous benefits, it also presents challenges, particularly when manufacturing automotive aftermarket parts that need to meet strict quality and design requirements. Understanding these challenges and how to address them is essential for delivering reliable, high-quality parts.
Meeting OEM Standards
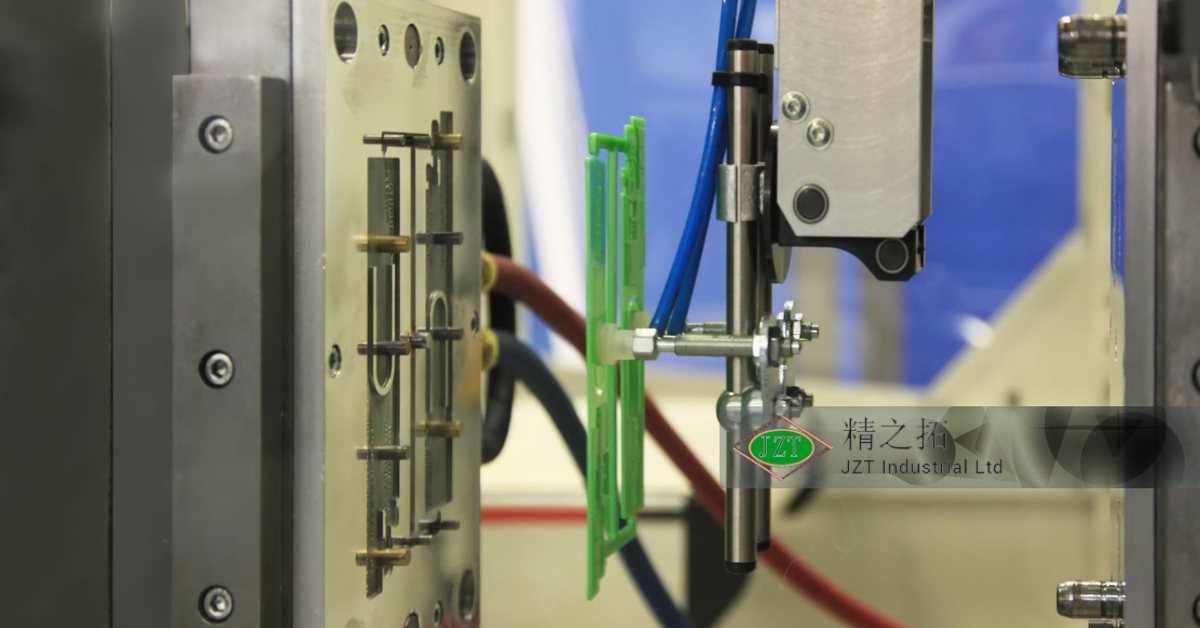
For aftermarket parts to be successful, they often need to match or exceed the quality and specifications of OEM parts. Meeting these standards requires precise control over every aspect of the injection molding process, from material selection to mold design and processing parameters. Quality control systems, such as regular inspections and automated monitoring, help ensure that each part meets OEM standards, making injection molding a trusted method for aftermarket production.
Material and Production Costs
Balancing quality with affordability is a key challenge in the aftermarket industry, where consumers expect high-quality parts at competitive prices. Although high-performance materials may increase durability, they can also raise production costs. Manufacturers address this challenge by selecting cost-effective materials that still meet part requirements, optimizing the molding process for efficiency, and adopting sustainable practices that reduce waste. These strategies help control costs while maintaining part quality.
Complex Design Requirements
Some automotive parts have intricate designs with complex geometries, which can be challenging to produce using standard injection molding techniques. Complex designs may increase cycle times, raise production costs, and complicate mold maintenance. Manufacturers address this by using advanced molding techniques, such as multi-material molding and overmolding, as well as simulation tools to refine mold designs before production. These approaches help produce complex parts without sacrificing quality or increasing costs excessively.
Minimizing Defects in High-Volume Production
Defects such as warping, sink marks, and flash can affect part quality, especially in high-volume production. Regular mold maintenance, optimized cooling channels, and controlled process parameters are all essential for preventing these defects. Additionally, real-time monitoring systems can detect any deviations from quality standards during production, allowing operators to make adjustments that minimize the occurrence of defects.
Sustainability Challenges
With growing interest in sustainable automotive solutions, there is pressure to incorporate recycled or biodegradable materials into injection-molded parts. While these materials support sustainability goals, they can present challenges related to durability, strength, and compatibility with traditional injection molding processes. Manufacturers address these challenges by developing new formulations, adjusting process parameters, and testing materials extensively to ensure they meet performance standards without compromising on sustainability.
Technological Innovations in Injection Molding for Automotive Aftermarket Parts
Technological advancements in injection molding are enabling new possibilities in the automotive aftermarket. Innovations in materials, process automation, and quality control are enhancing the performance, durability, and sustainability of injection-molded parts.
Advanced Materials for Enhanced Performance
New materials, such as heat-resistant thermoplastics and impact-modified polymers, are expanding the range of applications for injection-molded parts. These materials provide greater durability and resistance to extreme conditions, which is valuable for parts like engine components and structural supports. Advances in material science are also enabling the use of lightweight materials that improve vehicle efficiency while maintaining strength and durability.
Multi-Material and Overmolding Techniques
Multi-material molding and overmolding techniques allow manufacturers to produce parts with multiple materials in a single process. For example, a part can have a rigid core for strength and a flexible outer layer for impact absorption. These techniques are ideal for custom parts that require a combination of properties, such as soft-touch finishes or improved grip. Overmolding also enhances part functionality and reduces the need for assembly, which is beneficial in the aftermarket sector.
Rapid Prototyping and Tooling Advances
Rapid prototyping and tooling technologies, such as 3D printing, have revolutionized mold production by significantly reducing lead times and costs. Manufacturers can quickly test and refine molds before mass production, allowing for faster response to market demands. Rapid tooling enables manufacturers to adapt to changes in design or consumer preferences, ensuring that aftermarket products remain relevant and innovative.
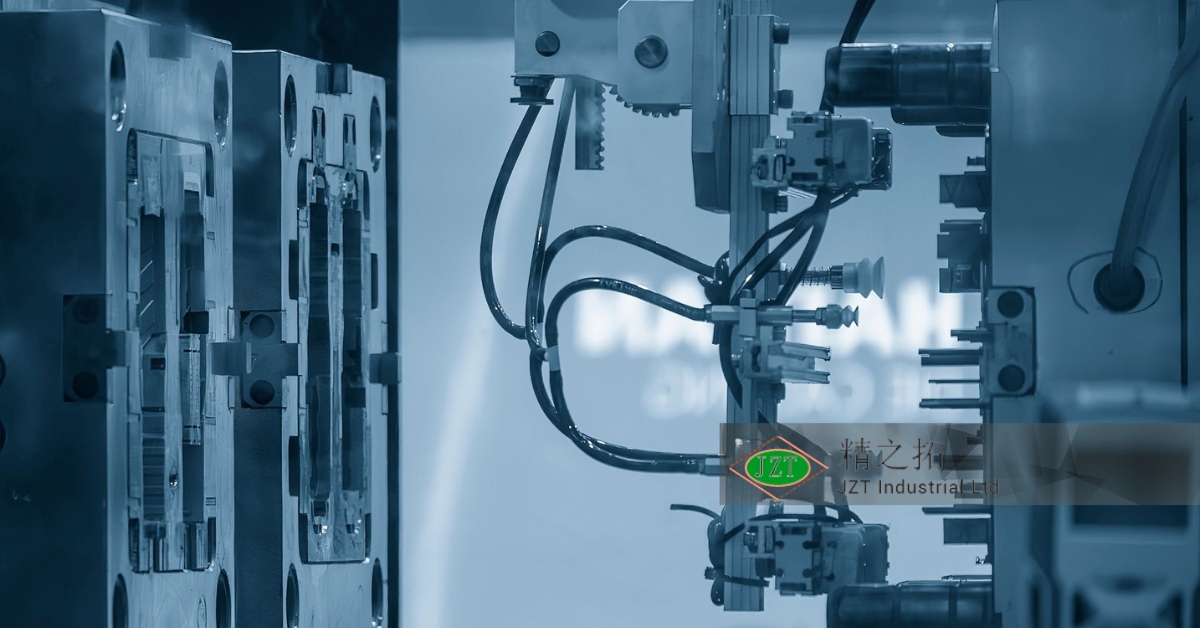
Automated Quality Control Systems
Automated quality control systems use advanced sensors and cameras to inspect parts in real time, identifying defects such as surface blemishes, dimensional inconsistencies, and material irregularities. These systems improve production efficiency by catching defects early, reducing waste, and ensuring that each part meets quality standards. In high-volume aftermarket production, automation is invaluable for maintaining consistency and quality across large batches.
Digital Twins and Simulation Tools
Digital twins and simulation tools allow manufacturers to create virtual models of the mold and part design, enabling them to analyze material flow, cooling rates, and potential defects before production. This predictive capability helps manufacturers optimize mold designs, reduce cycle times, and minimize material waste. Simulation technology ensures that each part meets exact specifications, making it a valuable tool for aftermarket parts production, where quality and fit are paramount.
FAQs on Injection Molding for Automotive Aftermarket Parts
1. What types of materials are used in injection molding for automotive parts?\
Common materials include ABS, polypropylene, glass-filled nylon, and other polymers that offer durability, impact resistance, and heat tolerance suitable for automotive applications.
2. How does injection molding reduce costs for aftermarket parts?\
Injection molding enables high-volume production at low per-unit costs after the initial mold investment, making it cost-effective for manufacturing large quantities of aftermarket parts.
3. Can injection molding meet OEM quality standards for aftermarket parts?\
Yes, with precise control over mold design, materials, and process parameters, injection molding can produce parts that meet or exceed OEM standards for quality and performance.
4. What types of automotive parts are typically injection molded?\
Injection molding is used to produce a variety of parts, including interior components (dashboards, trims), exterior components (bumpers, grilles), and functional parts (engine covers, brackets).
5. How are recycled materials used in injection molded automotive parts?\
Recycled plastics are increasingly being used to manufacture eco-friendly automotive parts, such as interior trims and exterior fascias, helping manufacturers align with sustainability goals.
Conclusion and Final Takeaways
Injection molding plays a pivotal role in the production of automotive aftermarket parts, offering an efficient, cost-effective solution for creating high-quality replacement and custom components. With its ability to deliver precision, durability, and design flexibility, injection molding enables plastic parts manufacturers to meet the diverse needs of the aftermarket industry. As consumer demand for personalization, performance upgrades, and sustainable products continues to grow, injection molding’s role in the aftermarket sector will only become more essential. For automotive parts manufacturers, partnering with an experienced injection molding provider ensures access to the latest technologies, materials, and design expertise needed to produce aftermarket parts that meet the highest standards of quality and innovation.